Ahmet Samet Özdilek, ProFAB: Open Protein Functional Annotation Benchmark
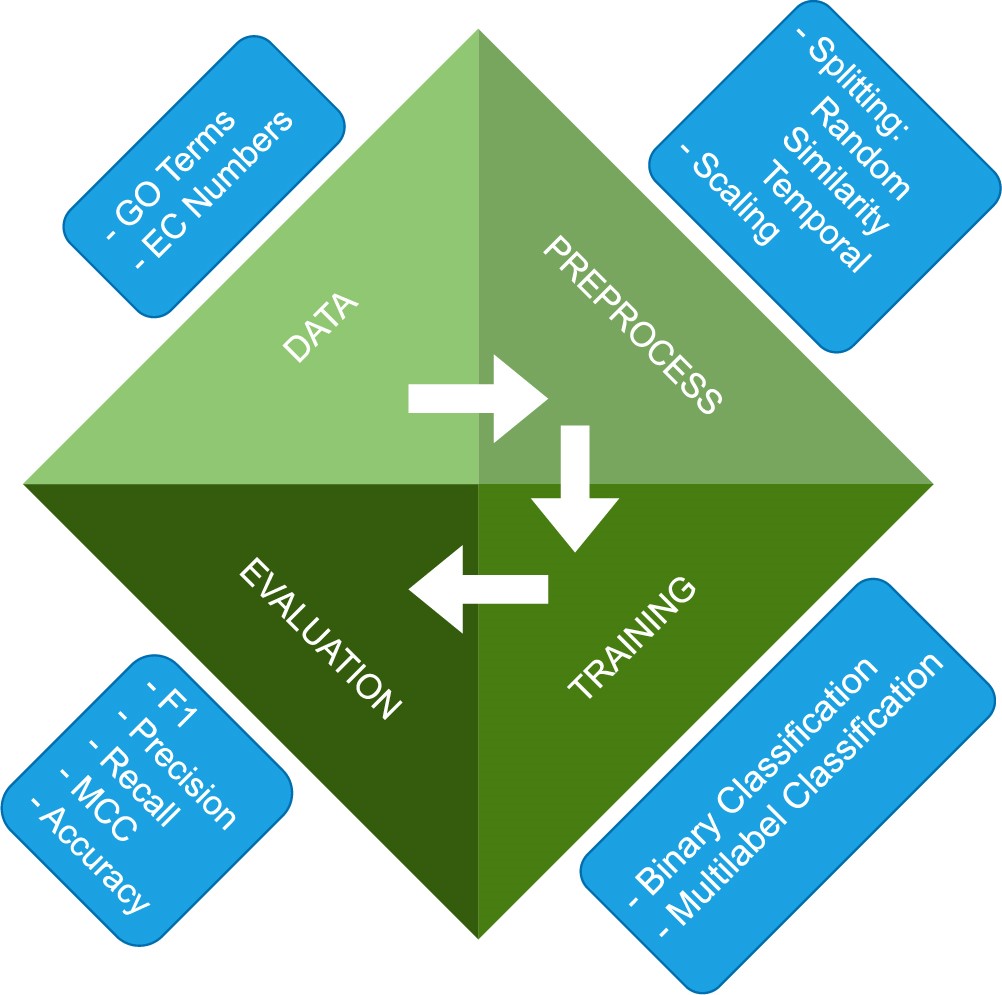
As number of proteins increases, computational methods play vital role for accurate function annotation. In spite of these methods, there are issues to compete which are reliable datasets and fair evaluation of performances. To address them, a fair comparison tool, ProFAB, Open Protein Functional Annotation Benchmark is developed. It aids computational and experimental researchers with its easy access to datasets and machine learning algorithms for protein function prediction using Gene Ontology terms and Enzyme Commission numbers.
Date: 21.08.2023 / 11:00 Place: A-212