Özgün Özkan, Impact of Scrum Tailoring on Technical Debt
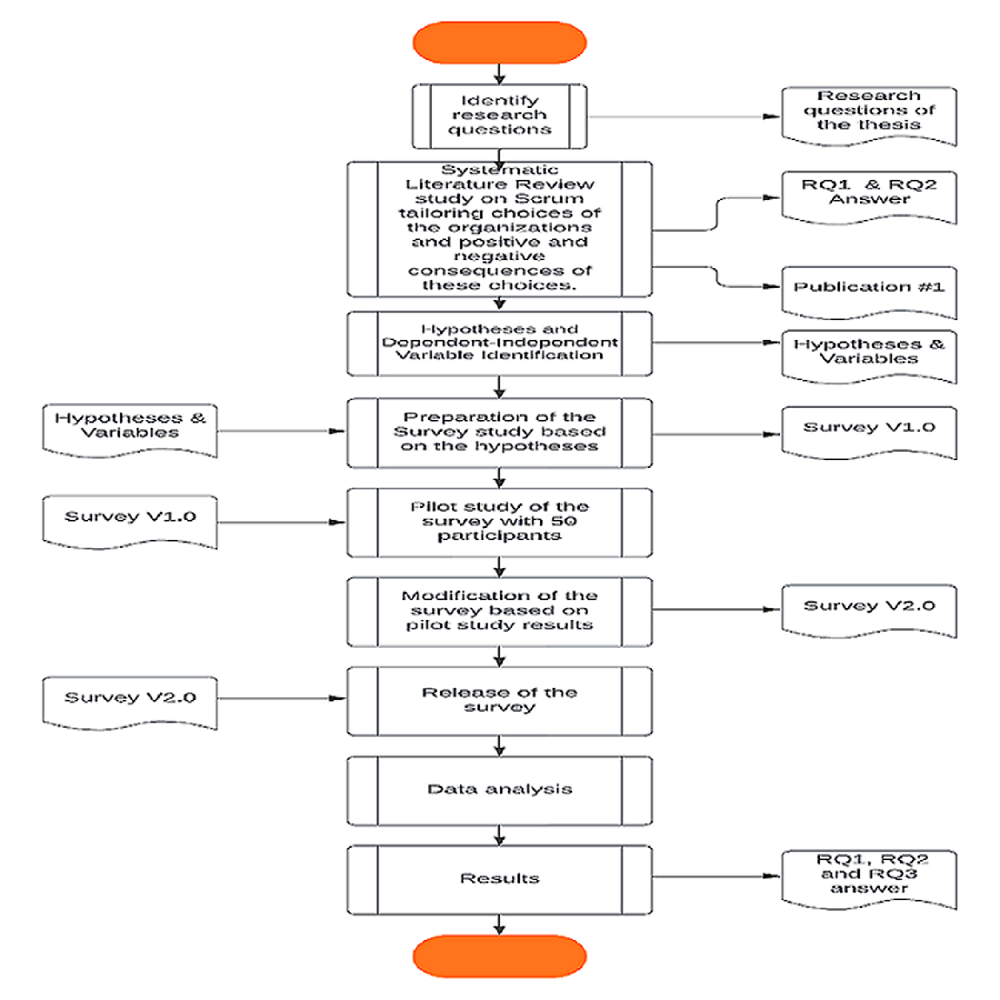
Among various Agile Software Development methods, Scrum is one of the most widely adopted one. The Scrum Guide clearly describes the Scrum events, artifacts, and roles. However, due to various project characteristics such as team size, team distribution, project domain, technology and requirement stability levels, Scrum practices need to be tailored. In this thesis, we analyze the various adaptations and tailoring choices of companies using Scrum. By incorporating evidence from literature and a survey study that is conducted among participants who use Scrum in their organizations, the impact of Scrum tailoring on technical debt will be analyzed.
Date: 24.01.2023 / 15:00 Place: B-116