Barış Deniz Sağlam, Knowledge Graph Augmented Multi-Hop Question Answering Using Large Language Models
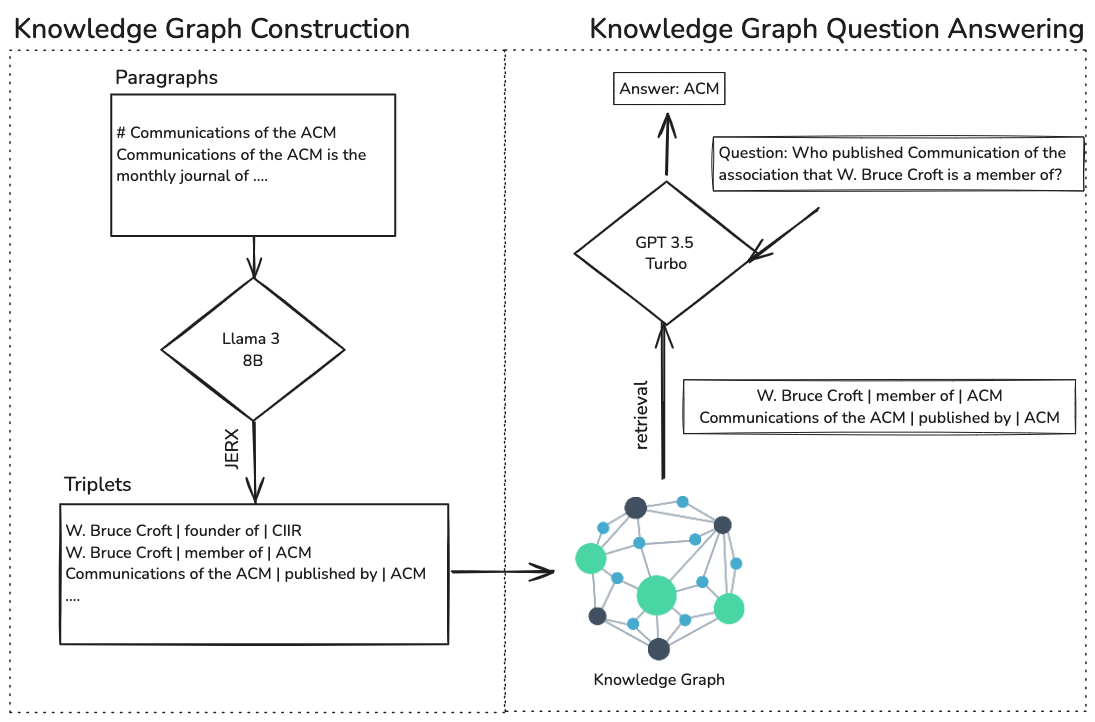
This thesis explores the use of small to medium-sized language models (LLMs) for multi-hop question answering, focusing on overcoming their limitations in knowledge and reasoning compared to larger models like GPT-4. The research explores using knowledge graphs to enhance these models' performance, specifically by integrating entity-relation triplets extracted from text. Techniques like supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning are evaluated for improving entity-relation extraction. A new prompting technique, Connect-the-Entities (CTE), is introduced to improve question answering performance with lower computational costs.
Date: 29.08.2024 / 10:00 Place: A-212